Oct 2025
Friction and Friction Coefficient
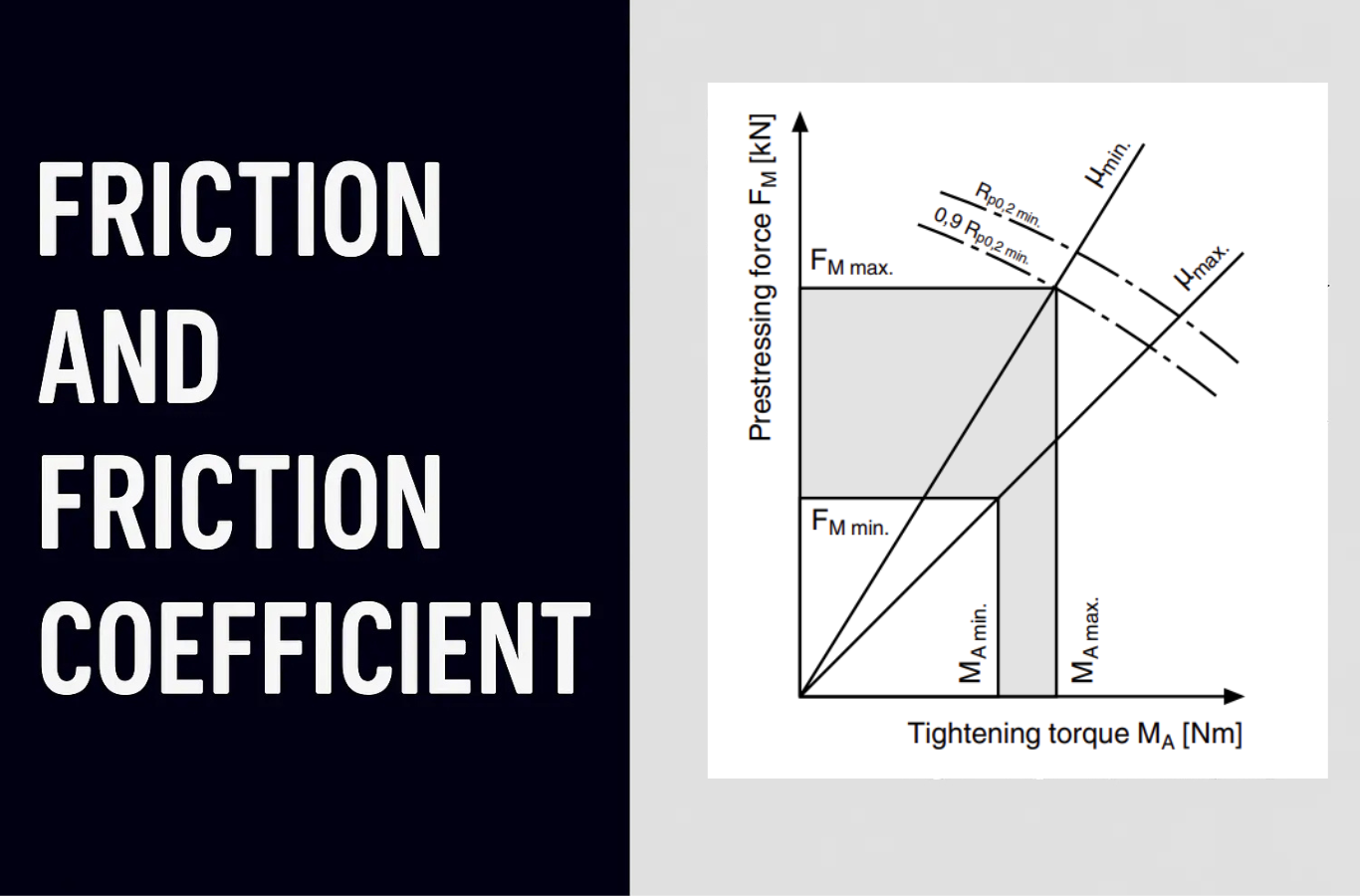
Friction plays an important role in how well screw connections stay tight and secure. The amount of friction, known as the friction coefficient, can change depending on the materials used, how smooth or rough the surfaces are, any coatings or treatments applied, and the type of lubrication used. These factors can make friction increase or decrease, so it’s important to keep the conditions as consistent as possible. If friction is too high or too low, the screw joint may not hold properly or could become damaged. By controlling surface finishes, using the right lubrication, and following proper tightening methods, we can make sure that screw connections remain strong, safe, and reliable.
| Friction coeff. class |
Range for µG and
µK
|
Typical examples for:
Material/surfaces |
Lubrication |
| A |
0.04–0.10 |
metallic, bright-polished
black tempered
phosphated
galvanized coatings such as Zn, Zn/Fe, Zn/Ni
zinc laminated coatings
|
solid lubricants such as MoS2, graphite, PTFE, PA, PE, PI in lubricating lacquers or in pastes
wax glazes
wax dispersions
|
| B |
0.08–0.16 |
metallic, bright-polished
black tempered
phosphated
galvanized coatings such as Zn, Zn/Fe, Zn/Ni
zinc laminated coatings
Al and Mg alloys
|
solid lubricants such as MoS2, graphite, PTFE, PA, PE, PI in lubricating lacquers or in pastes,
wax glazes, wax dispersions, greases, oils (as-delivered condition)
|
|
|
hot-dip galvanized |
MoS2, graphite, wax dispersions
|
|
|
organic coatings |
with integrated solid lubrication or wax dispersion |
|
|
austenitic steel |
solid lubricants or waxes; pastes
|
| C |
0.14–0.24 |
austenitic steel |
wax dispersions, pastes |
|
|
metallic, bright-polished
phosphated
|
as delivered state (lightly oiled) |
|
|
galvanic coatings such as Zn, Zn/Fe, Zn/Ni
non electrolytically applied zinc
adhesive
|
none |
| D |
0.20–0.35 |
austenitic steel
galvanic coatings such as Zn/Fe
hot-dip galvanized
|
oil
none
|
| E |
>= 0.30 |
galvanized coatings such as Zn/Fe, Zn/Ni
austenitic steel
Al and Mg alloys
|
none |
µG = coefficient of friction in the thread
µK = coefficient of friction in the head bearing area
µT = coefficient of friction at the interface